7.0 KiB
Getting Started of QEMU (Windows)
The development of embedded software is inseparable from the development board. Without physical development boards, similar virtual machines like QEMU can be used to simulate the development board. QEMU is a virtual machine that supports cross-platform virtualization. It can virtualize many development boards. To facilitate the experience of RT-Thread without a development board, RT-Thread provides a board-level support package (BSP) for QEMU-simulated ARM vexpress A9 development board.
Preparations
- Download RT-Thread Source Code
- Download Env Tool
- Install Git on your PC
Instructions for the Env tool
When using Env tools, you need to enter the corresponding BSP directory in the Env terminal.
Configuration
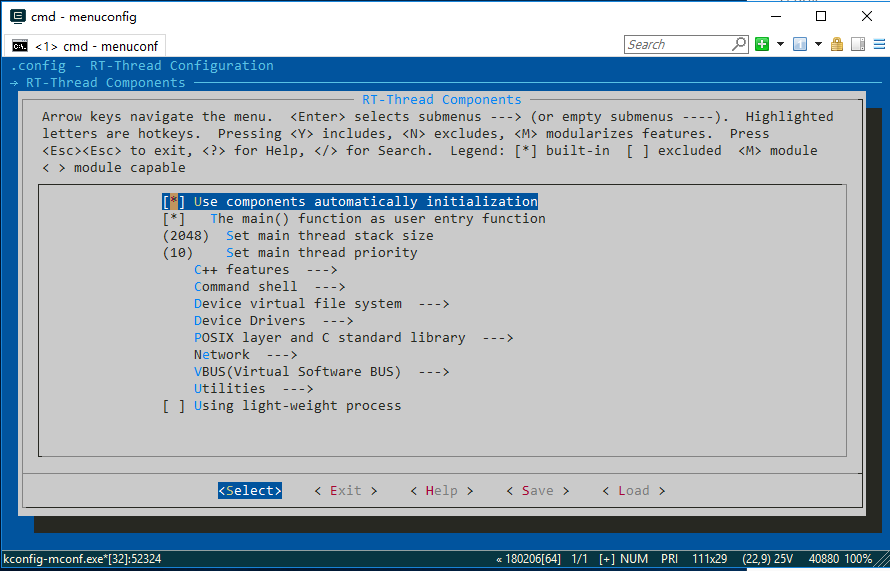
menuconfig
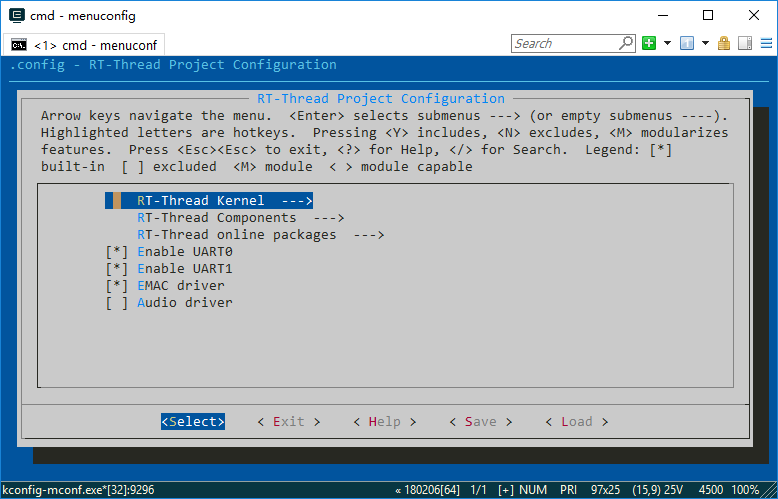
Type the menuconfig command in the Env terminal to enter the configuration interface, and then configure the BSP:
You can use the keyboard ↑ key and ↓ key to look up and down menu items, use the Enter key to enter the selected directory, use the Space key to select or cancel bool variables, and use the Esc key to exit the current directory.
Acquisition of software packages
pkgs --update
If a package is selected in menuconfig, download the package using the pkgs --update command (Git needs to be installed)
Compile
scons
Compile using the scons command.
Generate IDE's Project Files
scons --target=xxx
If you use the MDK or IAR IDE for development, you need to regenerate project files to make the configuration work after the configuration is completed. The command is scons --target=xxx, as shown below, which is the generation of IAR project, MDK4 project and MDK5 project.
scons --target=iar
scons --target=mdk4
scons --target=mdk5
Introduction of QEMU BSP Catalogue
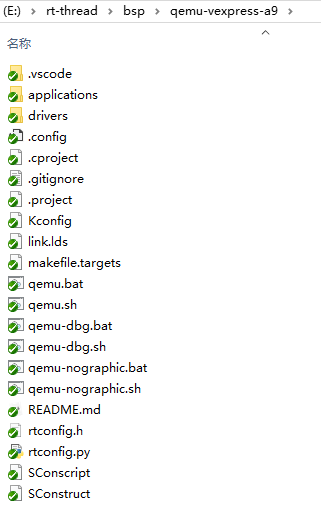
The board-level support package (BSP) provided by RT-Thread simulates ARM vexpress A9 development board is located in the qemu-vexpress-a9 folder under the BSP directory of RT-Thread source code. This BSP implements LCD, keyboard, mouse, SD card, Ethernet card, serial port and other related drivers. The contents of the folder are shown in the following figure.
The main files and directories of qemu-vexpress-a9 BSP are described as follows:
| Fles/Directories | Description |
|---|---|
| .vscode | configuration file of vscode |
| applications | User application code directory |
| drivers | The underlying driver provided by RT-Thread |
| qemu.bat | Script files running on Windows platform |
| qemu.sh | Script files running on Linux platform |
| qemu-dbg.bat | Debugging script files on Windows platform |
| qemu-dbg.sh | Debugging script files on Linux platform |
| README.md | Description document of BSP |
| rtconfig.h | A header file of BSP |
Compile and Run
Step 1. Use the scons Command to Compile the Project
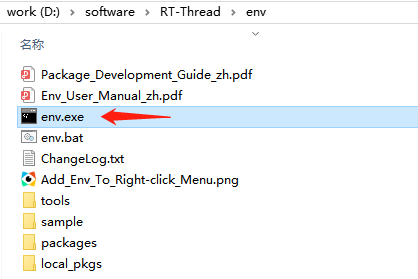
Open the Env folder and double-click the env.exe file to open the Env console:
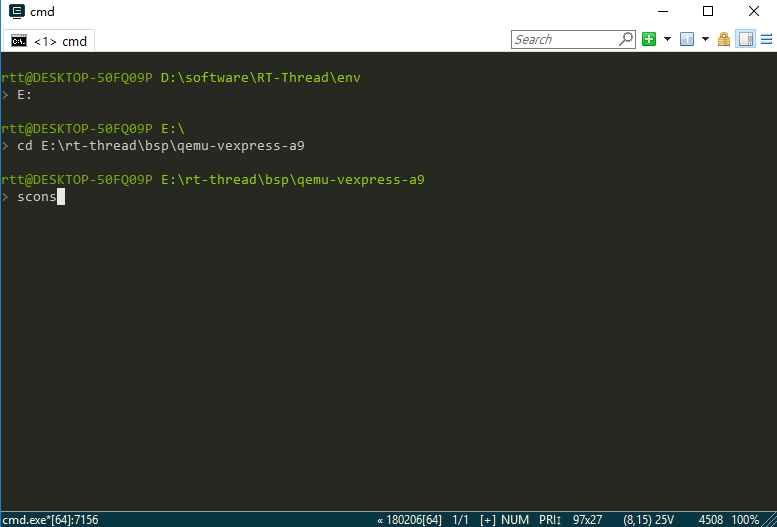
Switch to the QEMU BSP directory and enter the scons command to compile the project. If the compilation is correct, the rtthread.elf file will be generated in the BSP directory, which is a target file required for QEMU to run.
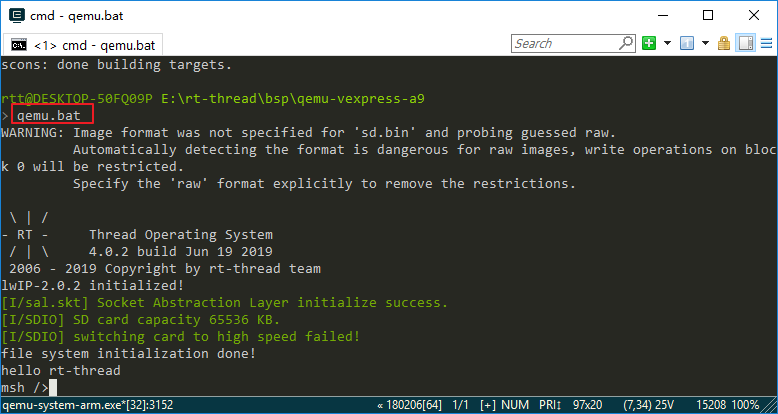
Step 2. Use the qemu.bat Command to Run the Project
After compiling, type qemu.bat to start the virtual machine and BSP project. qemu.bat is a Windows batch file. This file is located in the BSP folder, mainly including the execution instructions of QEMU. The first run of the project will create a blank sd.bin file under the BSP folder, which is a virtual SD card with a size of 64M. The Env command interface displays the initialization information and version number information printed during the start-up of RT-Thread system, and the QEMU virtual machine is also running. As shown in the following picture:
Run the Finsh Console
RT-Thread supports Finsh, and users can use command operations in command line mode.
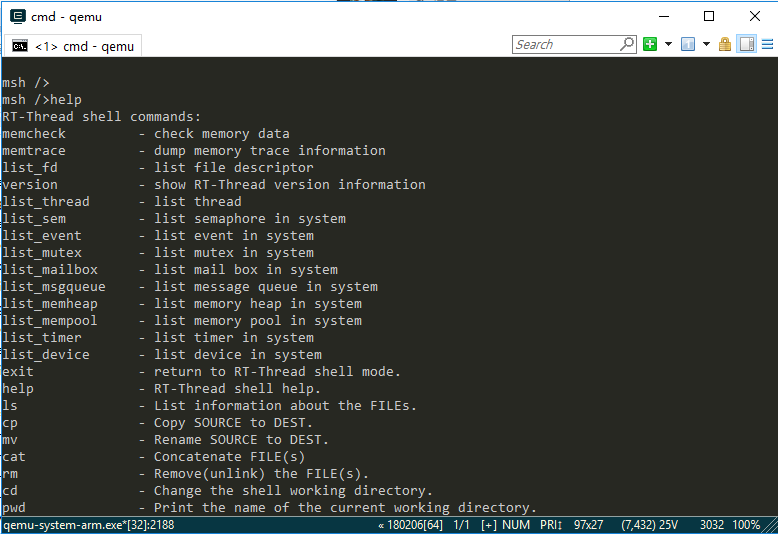
Type help or press Tab to view all supported commands. As shown in the figure below, commands are on the left and command descriptions are on the right.
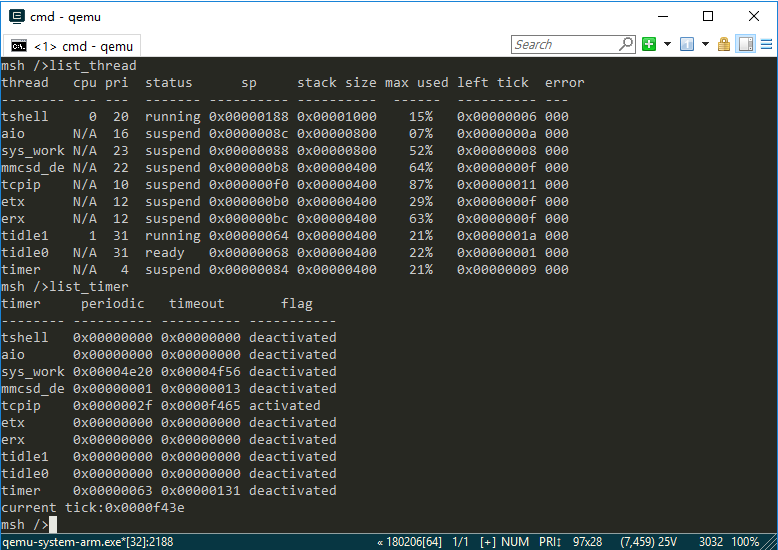
For example, by entering the list_thread command, you can see the currently running threads, thread status and stack size; by entering the list_timer, you can see the status of the timers.
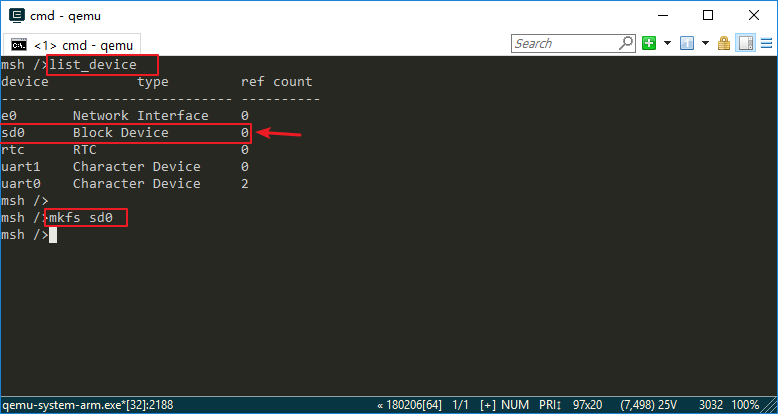
Run the File System
Type list_device to view all devices registered in the system. You can see the virtual SD card "sd0" device as shown in the following picture. Next, we can format the SD card using the mkfs sd0 command, which will format the SD card into a FatFS file system. FatFs is a Microsoft fat-compatible file system developed for small embedded devices. It is written in ANSI C, uses abstract hardware I/O layer and provides continuous maintenance, so it has good portability.
For more information on FatFS, click on the link: http://elm-chan.org/fsw/ff/00index_e.html
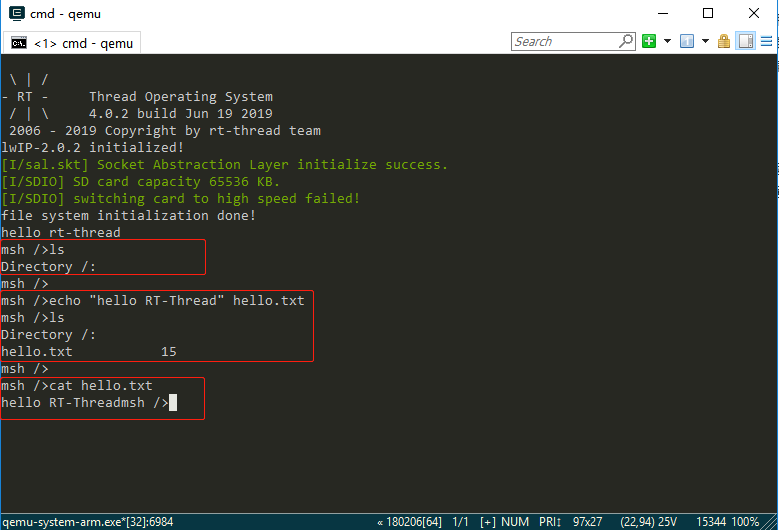
The file system will not be loaded immediately after the first formatting of the SD card, and the file system will be loaded correctly only after the second boot. So exit the virtual machine, and then restart the virtual machine and project by entering qemu.bat on the Env command line interface. Entering ls command, you can see that the Directory directory has been added, the file system has been loaded, and then you can experience the file system with other commands provided by RT-Thread:
- ls: Display file and directory information
- cd: Switch to the specified directory
- rm: Delete files or directories
- echo: Writes the specified content to the target file
- cat: Displays the details of a file
- mkdir: Create folders
Please enter help to see more commands.
More Functions
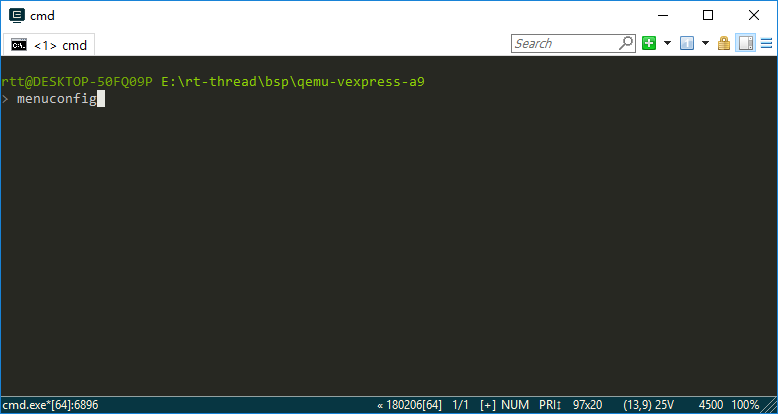
Open the Env tool in the BSP directory and enter the menuconfig command:
You can configure more functions in the configuration interface. After the configuration is completed, save the configuration first, and then exit the configuration interface:
- If you choose a package, you need to use the command
pkgs --updateto download the package. - Compile with
scons. - Then enter
qemu.batto run. - Use
helpto view all commands of the BSP. And then use the commands.